Chapter 2: How Search Engines Work: Inside the 3-Step Process
Need help with your SEO, marketing manager?
How Search Engines Work (And Drive Revenue for Your SMB)
You’ve learned the basics of SEO in Chapter 1 of our SEO Guide for Marketing Managers. Now, you’re ready to explore how search engines work and how their work impacts your bottom-line metrics, like leads, sales, and revenue. Keep reading to get started!
Table of Contents
- How do search engines work?
- What is the goal of search engines?
- How do search engines personalize results?
- How do search engines generate results?
- Why doesn’t my website show up in search results?
- How search engines work for your business in 2021
- What are search engines?
- How search engines work: Inside the 3-step process
- Why does getting crawled, indexed, and ranked matter?
- How to get your website crawled, indexed, and ranked in search results
- Glossary
How do search engines work?
Search engines work by gathering and categorizing information about web pages through crawling, indexing, and ranking. These search engines then return the most relevant pages in response to a user’s search query based on the information gathered through crawling webpages.
How search engines work: Achieving user satisfaction
How search engines work seems impersonal and technical, but that’s not the goal of search engines. Search engines aim to provide helpful content that answers a user’s question, whether they’re wondering how tall Mount Everest is, where to find tonight’s dinner, or the URL of Apple’s website.
That’s why search engines like Google use more than 200 ranking factors, including:
- Backlinks
- Keywords
- User interactions
- And more
It’s also why search results continue to evolve as search engines grow their indexes and users shift their preferences.
How search engines work: Personalizing search results
Search engines rely on more than their index to generate search results — they also rely on users. With information like a user’s location, preferred language, current device, and even search history, search engines like Google can deliver highly relevant results.
For example, someone searching for “sushi near me” will see search results based on their location, like sushi restaurants in Los Angeles, California. In comparison, someone searching in Houston, Texas, will see a list of sushi restaurants in that area.
How search engines work: Generating search results
You know how search engines work at a broad level, but what happens when someone makes a search?
The step-by-step process is as follows:
- A user enters a search query, like “how to tie a tie”
- A search engine references its index for content relevant to “how to tie a tie”
- A search engine generates results based on its algorithm and known user factors, like the user’s preferred language
The process doesn’t stop here, though.
Search engines like Google also monitor how users interact with search results. If someone visits a website from the search results but then returns, that registers as pogo-sticking, which can signal that a search result isn’t relevant.
Depending on how often this happens, Google may adjust its results for “how to tie a tie.”
7 reasons your company’s website doesn’t show up in search results
Is your company’s website still missing from search results?
Check for the following issues, which are some of the most common culprits for indexing issues:
- Your txt file accidentally excludes your entire site or pages you want indexed
- Your noindex tag accidentally instructs search engines to not index your page
- Your page URL returns a 404 error
- Your page contains duplicate content
- Your page contains thin content
- Your page delivers a poor user experience, like with spammy or low-quality content
- Your website got penalized, which you can check in Google Search Console
If you’re looking for a quick answer as to why your website doesn’t show up in search results, try SEO Checker. This free tool will provide an overview of your indexing status in 60 seconds, plus analyze your website’s SEO.
You can also request an SEO audit if you’re still struggling with indexing your site.
How search engines work for your business in 2024
In 2024, search engines work using web crawlers and advanced algorithms to crawl, index, and organize the web’s information. The process revolves around web crawlers, which crawl pages that the search engine adds to its index and then organizes and delivers to users via its search algorithm.
That’s an overview of how search engines work, but how do they work for businesses like yours?
Search engines serve as one of your company’s best team members because:
- 93% of online experiences start with a search engine
- 51% of users discover a new company or product after using a search engine
- 40% of revenue gets captured by organic traffic, which comes from search engines
With a search engine like Google, your business can capture more traffic, which translates to more leads, sales, and revenue when you optimize your website for the kinds of searches your target audience makes when moving through the modern-day buying funnel.
Are search engines working for your business, though? Find out in 60 seconds with our free tool, SEO Checker, which will audit your website, report on its crawling and indexing status, and score its level of search engine optimization (SEO).
Or, keep reading to learn more about what search engines are and how search engines work!
What are search engines?
Search engines are the primary tool people use to access websites and pages on the Internet. Without search engines, you could only find web pages by following a hyperlink or knowing the exact URL.
With search engines, discovering the answer to “What is EVOO?” is as simple as typing the question (it’s an acronym for extra virgin olive oil, by the way).

The five most popular search engines today are:
- Bing
- Yahoo!
- Baidu
- Yandex
These search engines all work in similar ways, but we’ll focus mainly on the most popular search engine, Google, for this page.
How search engines work: Inside the 3-step process
If you’re looking to understand how search engines work in-depth, then read this section. You’ll get an inside look at the three-step process that makes search results — and using search engines to drive revenue — possible.
1. Crawling
First, search engines work by crawling publicly available pages on the Internet. Search engines use web crawlers (also called bots or spiders) to find these public web pages and eventually index those pages.
Web crawlers work by:
- Finding pages: Crawlers first find and download web pages. They use links to discover new pages, much like users do. When a spider comes across a new link, that link leads to a new page the crawler can crawl.
- Scraping pages: When spiders arrive on a page, they make a copy of the page. They then look through the content and HTML to identify keywords and phrases that can help determine the page’s context.
The web crawlers use that information to decide whether to add that page to the search engine. They also list all the links on the page and queue the pages associated with them for crawling.
Web crawlers don’t just crawl a page one time, either.
Instead, web crawlers work non-stop to crawl and recrawl the uncountable number of web pages on the Internet. Doing so allows search engines like Google to have the most up-to-date versions of the pages.
Additionally, spiders have crawl budgets.
A crawl budget, simply put, is the number of pages on your site spiders crawl through and index before leaving, as well as which pages get crawled.
Crawl budgets take into account the limit Google sets on how often to crawl your site (based in large part on how frequently it’s updated and its popularity).
Google puts a limit on the number of pages crawled in one sitting to lighten the load on servers. If spiders scrape your site too fast or too often, it can bog down your servers, especially if your site contains thousands of pages.
2. Indexing
After the web crawlers work to read a page, they process and submit the information into an extensive database called a search index.
Search engines each create an index of online pages. Google, for instance, doesn’t rely on Bing’s index to generate search results. The index works similar to a library catalog. It’s a massive list of categorized entries that include all the information that crawlers scraped from the web.
Each page gets an entry so search engine algorithms have easy access to its contextual information. Using their massive indexes, search engines like Google quickly and accurately locate pages with relevant information.
3. Ranking
After the indexing phase comes ranking.
Search engines show results to users when they search but search engines can’t show all the pages it has in its index. Instead, it must choose which pages to place in results and the order in which these listings appear.
Search engines must then use the index’s information to accurately pull search pages with relevant information to show in searches. They also must determine how those pages rank according to relevance.
This problematic and arbitrary task is made easier with strict factors defined by search engine companies. These factors help search engines determine page relevancy.
These algorithms determine relevance by looking at:
- Keywords: Keywords are the phrases that users search for on search engines. Search engines look for the exact and related keywords when crawling online pages. Based on your page’s keywords and content, as well as other factors, search engines determine where your page ranks.
- Backlinks: Whenever another site on the web links to your page in their content, it’s called a backlink. Search engines like Google will use backlinks to determine the relevance of your page based on what pages link to your content. Google’s algorithm, PageRank, looks at the quality and quantity of backlinks to determine your rank.
Ranking involves more than just keyword selection and backlinks. Other factors focus on user experience, which strongly impacts how Google ranks search results. These factors include:
Google takes all these factors into account when ranking your site. Google’s algorithms use incredibly advanced artificial intelligence, which is adept at identifying what people want to see when searching.
Google BERT, for example, was an algorithm update Google performed in 2019. The update focused on improving the algorithm’s ability to understand what people mean when they enter search queries.
Through machine learning and natural language processing, BERT can better understand the context of all the words in a search query. With the update, Google can more easily understand things like synonyms and misspellings.
Why does getting crawled, indexed, and ranked well by search engines matter?
Less than 50% of businesses use search engine optimization.
That’s surprising because getting crawled, indexed, and ranked well by search engines is critical to growing a company, whether a startup or an enterprise, in 2024. When you exclude search from your marketing strategy, you exclude yourself from valuable leads, sales, and revenue.
Here are a few reasons why — and how — search engines generate business growth:
Buyer journeys happen on search engines
More than 90% of online experiences start with a search engine, which means when someone wants to find a new barber, upgrade their coffee machine, or get proposals for their company’s next project, they turn to a search engine like Google.
Even if your transactions happen offline, people use search to discover businesses in their area.
Research shows that four in five consumers use search engines to find local information. Not to mention, 76% of people who make location-specific searches visit a related business within a day, which is one reason 80% of local searches convert.
Search engines maintain an impressive close rate
Search engines help people discover your business, making it possible for your company to nurture more leads and close more sales. Compared to traditional marketing close rates, search offers a massive improvement with a 14.6% close rate — traditional marketing’s close rate is less than 2%.
Traditional marketing frequently fails against digital marketing strategies like SEO because SEO:
- Helps users find relevant information that makes converting possible
- Reaches users when they’re interested in a product, service, or topic
- Nurtures users through every stage of the buying funnel, from awareness to purchase
Essentially, with search, you can reach your dream customer at the right time with the right content. That perfectly timed connection makes a significant difference in capturing more leads, sales, and revenue.
Search engines connect your business with its target audience 24/7
People search around the clock. That’s why search engines serve as fantastic team members.
With search engine optimization, your company can capture valuable traffic 24/7, without the cost of overtime. Instead, your website serves as a hub for potential clients to learn about your business, contact your team, and even purchase your products — if you maintain an ecommerce site.
How to get your company’s website crawled, indexed, and ranked in search results
You know how search engines work, as well as what a search engine does, but do you know how to get your company’s website crawled, indexed, and ranked in search results so you can capture all the benefits of SEO?
If not, check out this walkthrough!
How to get your company’s website crawled
Having your site crawled is the ticket to Internet visibility. You want to make sure that spiders can easily access your site because your site needs to get crawled before it can ever appear in search.
It’s as simple as:
No crawling on your site = No appearance in search results
If you have a new website (or even a new page on your site), there are a few tricks you can do to get Google to crawl your site quickly:
Submit your URL to Google Search Console
You can request a crawl from Google by submitting your URL in the Google Search Console. Providing your URL allows Google to find your site faster.
You can submit your URL by heading to the URL Inspection tab in your Search Console account. Then select the “Test Live URL” option and click “Request Indexing” if the test shows your URL hasn’t gotten indexed.
Include internal links in your new page to older content (and vice versa)
Internals links are hyperlinks you place on your pages that link to other pages on your site with relevant information.
Internal links help spiders crawl your site by allowing them to travel from page to page more quickly. When internal links link to relevant content on your website, it can help Google better understand the context of your content.
In the same way, internal links also help your visitors navigate your page and find additional content.
Create an XML sitemap
Your XML sitemap contains information for Google on how often it should crawl individual pages on your site.
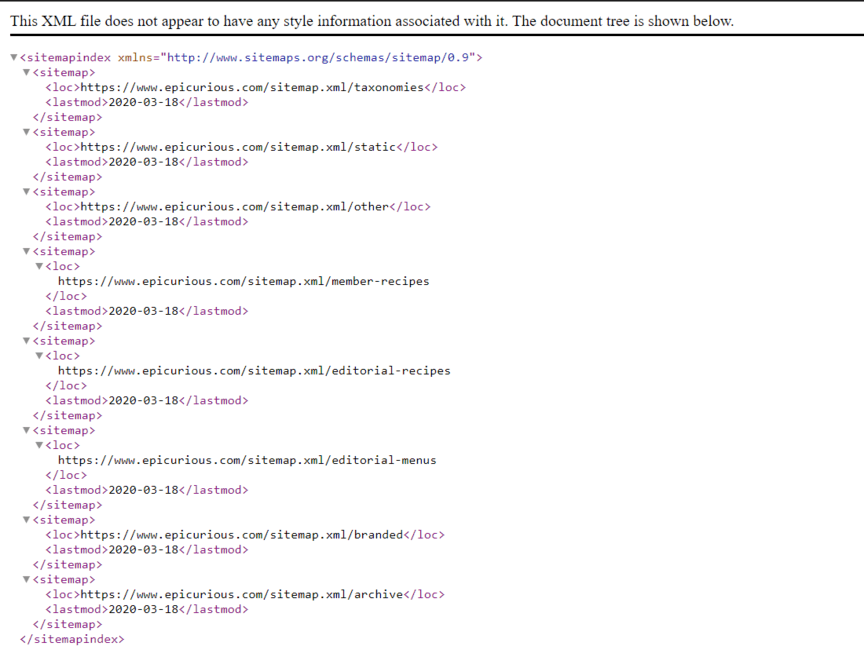
For example, let’s say you have a page for your blog and a page for FAQs. Your FAQs don’t change much, but your blog gets updated daily. Within your sitemap, you can tell Google that you want it to give your blog priority over your FAQ page.
Sitemaps also help spiders find and understand the level of importance you give the new pages you publish. You can request a crawl of your site by submitting your sitemap to Google’s Search Console, as well.
You aren’t limited to one sitemap, either. You can have multiple, such as a central sitemap and a sitemap for your blog.
Create a robots.txt file
Your robots.txt file is a list outlining suggested crawling instructions for Google and other crawlers. This file, however, doesn’t control what search engines index or how they do it. Robots.txt just lets Google know you’re preferences towards crawling individual pages on your site.
There may be some cases that you would want to suggest an opt-out on having particular pages on your site crawled.
For instance, if you run an online store, you probably wouldn’t want Google to crawl your customers’ accounts. Or, if you happen to have multiple URLs for the same page on your site, you want Google crawling the page only once.
Limiting the pages that get crawled also helps your site manage which pages count towards your crawl budget.
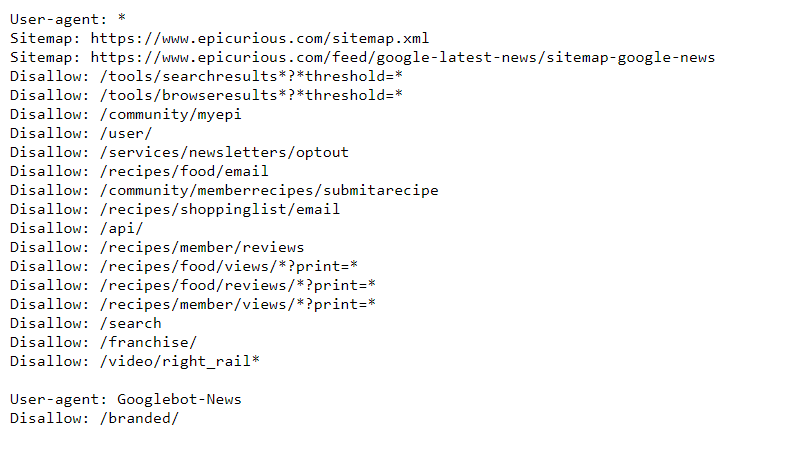
In your robots.txt file, you can choose which pages on your site allow or disallow crawling, though search engines can still index your pages if someone else linked to your page.
You can even limit crawling by identity. So, if you didn’t want Bing to crawl a page but wanted Google to have access still, you would put it in your robots.txt file.
You can check how your robots.txt file looks by typing it after your domain name like this:
examplesite.com/robots.txt
How to get your company’s website indexed
Having your pages indexed is a requirement for Google to rank them in search results. If your pages aren’t indexed, they won’t do you very much good since people won’t find them. Your pages won’t pull in any traffic.
If you do not see your page on search, you can check out these simple search engine indexing strategies:
Check if your page is indexed using the “site:” operator
You can check all the pages that Google has indexed by conducting a “site:” search for your URL. Just type in “site:[your site domain name].com” into Google’s search bar, and it will pull up all the pages that Google has on your site.
You can also perform a “site:” search to find content on your site that matches specific keywords, which is useful when looking to see if Google has indexed a particular page. The format goes “site:exampleurl.com example keyword.”
Crawling and indexing generally take a few days, so don’t be too worried if your recently published page doesn’t immediately show up in search.
Check your page’s status in Google Search Console
If it’s been a while and you’re still not seeing your pages using the “site:” search operator, it’s likely that your site is not in the search engine’s index and probably hasn’t gotten crawled yet.
You can double-check your page’s status using the “Test Live URL” option under the URL Inspection tab in your Search Console account. If your page hasn’t gotten crawled yet, you can request indexing. This process may take a few days to accomplish.
Also, check to see if there is a reason that Google isn’t indexing your content.
Some problems that could prevent indexing include:
- You have crawl errors you need to fix on your site that prevent Google from crawling your page
- You have JavaScript issues that can prevent crawling
- You have duplicate content on your site (Google won’t know which to rank)
- You’re using black hat optimizing practices
Check if you’re directing Google to not index
Like crawling, you can direct Google to not index pages on your website, such as admin pages and internal search.

To do so, you can either include a “noindex” tag in your robots.txt like this:
- Noindex: /page-you-specify
Or include the “noindex” tag in the HTML of your page like this:
- < meta name=”robots” content=”noindex” />
In some cases, these specifications could be what is causing your page not to be indexed when you want it to be, so be sure to double-check.
How to get your company’s website ranked well in search results
By ranking pages, Google helps people find the information they’re looking to find.
Search engine ranking means a couple of things to online sites.
Your rank in search is a huge determiner for how much visibility your content gets. Take a look at these three stats:
- The first page of search receives 95% of search traffic.
- The number one spot in search gets 33% of internet traffic.
- The top three search results get 75% of all clicks.
If your page doesn’t rank on the first page, you’re getting slim pickings for search traffic. Not having a high rank in search doesn’t just lower the traffic you get — it also decreases your ability to drive sales and conversions.
Rank also indicates to your audience your brand’s authenticity. The more you rank for various keywords, the more authentic people will view you.
Here are some strategies to improve your site’s rank in search results.
Perform keyword research
Keyword research allows you to provide the most relevant content to your users, which helps you rank higher in searches.
Take some time to study what users mean when they enter keywords into search engines. You can do that by researching what content currently ranks for the keywords you are targeting because Google’s algorithms do a good job of understanding what people want to know.
When performing keyword research, make sure to target long-tail keywords. Long-tail keywords are longer phrases, often three words or more. They can include locational keywords like “near me,” question keywords like “what is” or “how,” and conversational keywords from voice search.
Long-tail keywords work well for ranking in search results because they’re less competitive to rank for than short-tail keywords while still generating most of your site’s traffic.
Build a link building strategy
Your link building strategy involves techniques that encourage other sites to link to your site. Much of your link building strategy will center around producing content that your readers find valuable. If you create good content, people will be more willing to link to it.
Other link building techniques include:
- Creating tools like industry calculators that your users can use to provide relevant insight
- Asking prevalent people in your industry to link to your content
- Write guest content for other sites
- Spread awareness of your content on social media
Make your content user-friendly
You want your audience to enjoy the time they spend on your website. User-friendly content acts as a significant factor in the definition of valuable content. Google ranks search results with user-friendly content higher, and users will spend more time on your site.
Make your content user-friendly by:
- Answering the questions quickly, clearly, and concisely
- Use relevant headings to organize topics
- Break up your paragraphs into two to three sentences so they’re easier to read
- Utilize bulleted and numbered lists to users and search engines can find valuable information
- Place images, videos, and infographics to improve your content’s engagement levels
6 helpful definitions for learning how search engines work
Before learning about the three-step process behind how search engines work, check out this mini-glossary. You’ll learn about some of the most common terms for discussing search engines, like crawling, indexing, and more.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| 1. Search engine index | A search engine index is like a library but a library of websites and their pages. When a search engine generates results, it generates the results from its index. |
| 2. Crawlers or spiders | Search engines build indexes with crawlers or spiders. These robots crawl the web and bring what they find to a search engine and its index. |
| 3. Crawling | Crawling describes the process of crawlers or spiders to index the web. They ‘crawl’ publicly available pages on the web and then bring the information back to a search engine’s index. |
| 4. Search engine results page (SERP) | A SERP is the results page generated from a user’s query and a search engine’s index. Multiple factors influence a SERP, from the user’s location to your website’s speed. |
| 5. Search engine ranking | Search engine ranking describes where a page ranks in a search result for a query, like “espresso machine maintenance.” |
| 6. Search intent | Search intent describes the motivation behind a search. Someone searching “espresso machine maintenance, for instance, may want to learn how to maintain their machine or what it takes to maintain a machine — before buying one. |
Make search engines work for your business with professional SEO services
Search engines work every day to help people find what they need, whether it’s a new coffee maker, a plumber, or a service provider for their business. When you invest in SEO, which optimizes your site for search engines and users, you make search engines work for your company.
Search engine optimization takes time, skill, and effort, though, which is why many small-to-midsized businesses partner with an SEO agency like WebFX. As your partner, we’ll help your company build, implement, and manage an SEO strategy that contributes to your bottom line.
Already, we’ve helped our clients earn more than $6 billion in revenue in the past five years.
Start driving more revenue for your business with SEO by contacting us online (or giving us a ring at 888-601-5359) to speak with a strategist about our SEO services, which range from national SEO to local SEO to ecommerce SEO!

 Sarah Berry
Sarah Berry