What to read next
Understanding AI Cybersecurity for SMBs: Here’s What You Need to Know in 2025

The 5 Best AI Photo Editors That Make Image Editing a Breeze

What Is an RFI for Marketing? A Step-By-Step Playbook To Vetting Agencies Like a Pro

SEO for Doctors: How to Attract More Patients with a Smarter Search Strategy



 In other words, your carbon footprint directly relates to the amount of CO2 produced by daily activities. If you want to
In other words, your carbon footprint directly relates to the amount of CO2 produced by daily activities. If you want to 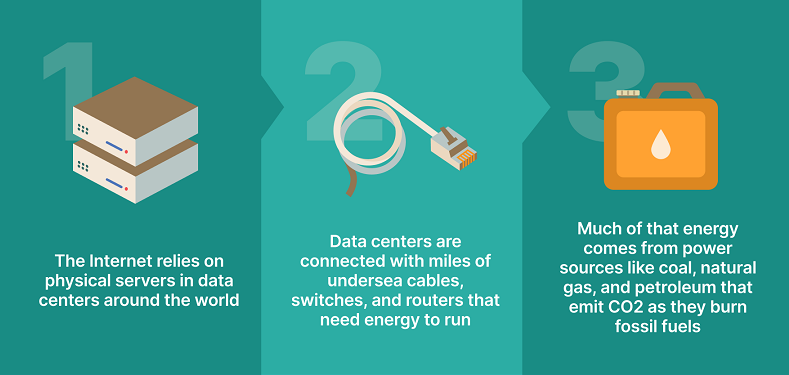 In addition, technology companies emit CO2 by manufacturing and shipping hardware like:
In addition, technology companies emit CO2 by manufacturing and shipping hardware like:




 As we see above, the U.S. ranks third in terms of Internet users, but it surpasses the second-ranked country, India, in terms of CO2 output. So, while there appears to be a slight correlation, many other factors impact
As we see above, the U.S. ranks third in terms of Internet users, but it surpasses the second-ranked country, India, in terms of CO2 output. So, while there appears to be a slight correlation, many other factors impact  Around the world, people watch 1 billion hours of YouTube videos every day. Watching YouTube videos produces six grams of CO2 per hour, resulting in 6 billion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 62 times!
Around the world, people watch 1 billion hours of YouTube videos every day. Watching YouTube videos produces six grams of CO2 per hour, resulting in 6 billion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 62 times! Around the world, people send and receive 306 billion emails every day. The average email (without a large attachment) produces 4 grams of CO2, resulting in 1.2 trillion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 12,000 times!
Around the world, people send and receive 306 billion emails every day. The average email (without a large attachment) produces 4 grams of CO2, resulting in 1.2 trillion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 12,000 times! Around the world, 1.7 billion people use Facebook every day. Using Facebook produces 0.8 grams of CO2 per user per day, resulting in 1.3 billion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 13 times!
Around the world, 1.7 billion people use Facebook every day. Using Facebook produces 0.8 grams of CO2 per user per day, resulting in 1.3 billion grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 13 times! Around the world, people conduct 3.5 billion Google searches every day. Each Google search produces 0.2 grams of CO2, resulting in 700 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 7 times!
Around the world, people conduct 3.5 billion Google searches every day. Each Google search produces 0.2 grams of CO2, resulting in 700 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 7 times! Around the world, people send 500 million tweets every day. Each tweet produces 0.2 grams of CO2, resulting in 100 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 7 times!
Around the world, people send 500 million tweets every day. Each tweet produces 0.2 grams of CO2, resulting in 100 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 7 times! Around the world, people send 18.7 billion text messages every day. Each text produces 0.014 grams of CO2, resulting in 261.8 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 3 times!
Around the world, people send 18.7 billion text messages every day. Each text produces 0.014 grams of CO2, resulting in 261.8 million grams of CO2 produced globally every day. That’s the same amount of CO2 produced by driving to the moon 3 times!



 These simple switches may seem insignificant, but they add up and play a key role in reducing our combined carbon footprint.
These simple switches may seem insignificant, but they add up and play a key role in reducing our combined carbon footprint.
