-
 9 min. read
9 min. read
-
 Sarah Berry
Sarah Berry Lead Web Marketing Consultant
Lead Web Marketing Consultant
- Sarah Berry is a Lead Web Marketing Consultant at WebFX. With more than 10,000 hours of experience, she offers practical insights and strategies you can use to grow your digital revenue. When she isn’t polishing her Time Magazine Person of the Year Award, she’s spending time with her flock of ducks.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is a powerful tool that simplifies the process of adding and managing website tags, allowing businesses to track and analyze their online performance more effectively.
How do you track and monitor your online marketing strategy, plus measure its return? If you’re like most businesses, you probably use Google Analytics. For simplified tracking management, however, many companies are switching to Google Tag Manager (GTM).
This sister product to Google Analytics makes tracking user activity and site performance easier for you and your team. What is Google Tag Manager, though? Keep reading to find out!
Plus, learn why you should use Google Tag Manager and how it works alongside Google Analytics. Even better, get a simple breakdown of this free tool’s advantages and disadvantages.
What is Google Tag Manager?
 Google Tag Manager is a free tag management tool that helps you create, manage, and launch HTML or JavaScript tags. These tags track analytics data on websites or mobile apps, as well as share that data with web analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
Google Tag Manager is a free tag management tool that helps you create, manage, and launch HTML or JavaScript tags. These tags track analytics data on websites or mobile apps, as well as share that data with web analytics platforms like Google Analytics.
What is the difference between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics?
While both free tools from Google, Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager handle different functions.
Google Tag Manager focuses on what data to track, when to log it, and where to send it. In comparison, Google Analytics houses data, which you can view and interpret via reports.
What does Google Tag Manager do?
With GTM, you can create custom tags, triggers, and variables in a container snippet (more on those below). These components streamline and automate the process of tracking user behavior, whether on your website or mobile app.
They also eliminate the time-consuming steps involved with tag tracking and tag management via Google Analytics. Google Tag Manager accomplishes these tasks by replacing manually coded tags on your site or app. If your website uses tracking tags for Google Analytics and Google Ads, for example, you can replace, update, and manage them with GTM.
Whenever you update these tracking tags, you can count on the changes going live immediately, versus copying-and-pasting the new code onto dozens of pages. In short, Google Tag Manager helps automate a process that used to rely on tedious manual steps.
6 crucial components to GTM
Before you decide to use GTM in your strategy, you need to understand its six core components:
| GTM Component | What It Does |
|---|---|
| Container Snippet | Houses your tags and lets you update tags automatically. |
| Tags | Tracks an action, like a purchase, and sends that data to a place like Google Analytics. |
| Triggers | Describes an action, like completing a purchase, that will launch the trigger’s respective tag. |
| Variables | Operates as a placeholder for a changing value, like a product price or URL. |
| Values | Describes a static and user-defined value, like a page URL, for a trigger. |
| Operators | Lists the required relationship between a variable and a value. When the variable and value meet the requirements, the trigger can fire. Once the trigger fires, the tag can collect and send the appropriate data to the designated platform, like Google Analytics. |
1. Container snippet
A container snippet plays a critical role in Google Tag Manager.  That’s because container snippets let you update page or app tags automatically. Instead of copying-and-pasting your latest tracking tag to a page, you can change the tag in Google Tag Manager.
That’s because container snippets let you update page or app tags automatically. Instead of copying-and-pasting your latest tracking tag to a page, you can change the tag in Google Tag Manager.
The container snippet will then update on your page. In every container, you will have the following:
- Tags
- Triggers
When you create a GTM account, you will need to have at least one container snippet.
2. Tags
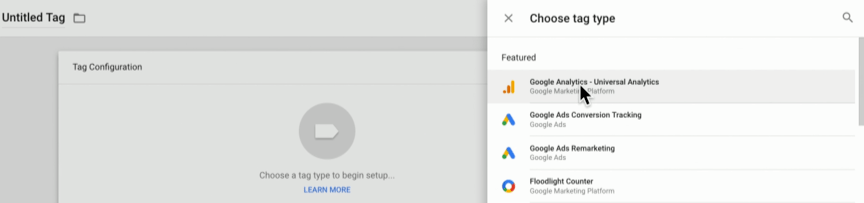 Tags also play a vital role in Google Tag Manager. In most cases, you will have a range of tags. Your tags describe what you want to track, as well as send to third-party website analytics tools, like Google Analytics.
Tags also play a vital role in Google Tag Manager. In most cases, you will have a range of tags. Your tags describe what you want to track, as well as send to third-party website analytics tools, like Google Analytics.
For example, your company may wish to monitor product purchases, video interactions, or conversions from a recent ad campaign.
3. Triggers
 Triggers serve as a core feature of GTM. With triggers, you tell Google Tag Manager when your tags should collect and send data to different applications. For example, you may want to track purchases for a specific product or page views for all your pages.
Triggers serve as a core feature of GTM. With triggers, you tell Google Tag Manager when your tags should collect and send data to different applications. For example, you may want to track purchases for a specific product or page views for all your pages.
You can specify those actions with a trigger. A trigger consists of three parts:
- Variables
- Operators
- Values
For accurate tracking, you can create multiple triggers for a single tag. No matter how many triggers you build, ensure they function as intended. If you skip testing your tags and triggers, you could discover months (or years) later that you’ve been collecting the wrong data.
Consequently, this can have a tremendous impact on your digital marketing and even advertising strategy.
4. Variables
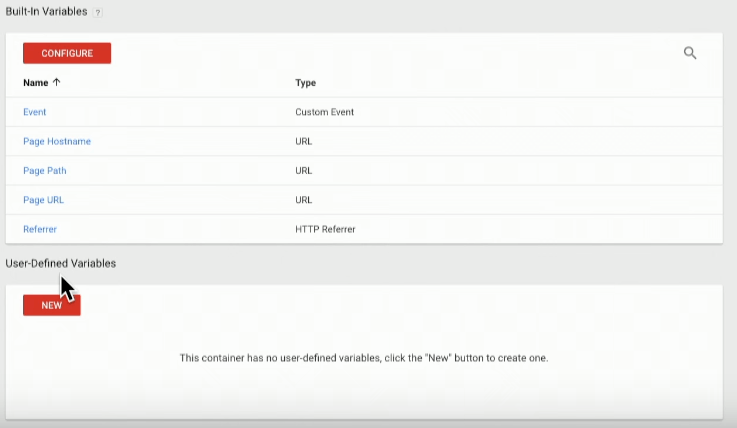 Variables serve as placeholders for values and include:
Variables serve as placeholders for values and include:
- Built-in variables
- User-defined variables
While built-in variables include pre-configured GTM variables, like following a certain page path, user-defined variables feature custom GTM variables. In most cases, these variables describe purchases, form completions, and more.
5. Values
 Values help you customize your triggers and data collection further. With values, you specify a value via a text field to check against your variable. Depending on your operator, your variable may need to equal your value to launch the trigger.
Values help you customize your triggers and data collection further. With values, you specify a value via a text field to check against your variable. Depending on your operator, your variable may need to equal your value to launch the trigger.
Or, it may need to have a lower value. As an example, look at the following variable, operator, and value for a trigger:
- Variable: {{url}}
- Operator: equals
- Value: /application-accepted.html
Due to these values, this trigger will only happen when the URL (the variable) equals /application-accepted.html (the value). A company could use this kind of trigger to track and separate conversions, like for applications and purchases.
6. Operators
 Operators are another essential component to Google Tag Manager. With operators, you define the relationship between a variable and a value. This relationship determines when a trigger can fire, which influences when you collect data via a tag.
Operators are another essential component to Google Tag Manager. With operators, you define the relationship between a variable and a value. This relationship determines when a trigger can fire, which influences when you collect data via a tag.
Again, you need to test this feature to ensure you track the right data. A few examples of operators include:
- “equals”
- “contains”
- “doesn’t contain”
You can also choose from additional operators, like “less than,” “matches RegEx,” and more.
4 advantages of Google Tag Manager
Google Tag Manager offers several perks, including:
1. Streamline collaboration
Whether your team collaborates via phone, video, or face-to-face, you need tools that make your life easier. Google Tag Manager is one of those. With GTM, your team can log in, view, and modify your tags instantly.
Plus, you can set user-specific permissions to provide everyone with the appropriate level of access.
2. Access third-party tags for convenient data tracking
Depending on your business, you may only use Google tags (like Google Ads and Google Analytics) to view your website or app data. As your company grows, though, you may find a need for third-party platforms, which is where this benefit of GTM becomes valuable. With GTM, you can create tags for a range of third-party platforms.
Your team can even create custom tags if needed. If you’re not technical, GTM also provides tag templates for its array of Google and third-party tags. You can use this handy feature to get started with Google Tag Manager fast.
3. Check for errors to fix problems fast
GTM does require some hands-on learning, which is why the platform features error checking. With error-checking, your team can look over your tags, triggers, and variables, and spot errors fast. Even if you have extensive experience with Google Tag Manager, this feature can save time and prevent incorrect data tracking.
4. Add and update tags in an instant
The most significant advantage of GTM comes from its ability to update your tracking settings fast. Whether you feature one or multiple container snippets across your site, you can count on Google Tag Manager to update the tags, triggers, and variables in those snippets the moment you update them. This feature eliminates the time-intensive process of copying-and-pasting new snippets onto pages.
2 disadvantages of Google Tag Manager
While GTM offers several benefits, it also comes with a few drawbacks, including these two:
1. Requires a developer background
Anyone can use Google Tag Manager, but it’s a new frontier for users without a developer background. This learning curve can make adopting GTM difficult. In some cases, it can even turn a company off from the entire idea.
Learning about variables, values, and operators — and then creating them — can seem intimidating and result in errors. That’s why Google Tag Manager includes an error-checker tool and a beginner’s course.
2. Involves a time-intensive migration process for large sites
Adopting and migrating over to GTM can become a massive project for companies with larger websites. That’s because you will need to remove existing tracking codes on site pages and replace them with your container snippet. If you don’t have a developer that can expedite this process, this project can demand a tremendous amount of time and resources.
If you have a 25- or 50-page site, copying-and-pasting the container snippet can be a tedious task. While there isn’t a workaround for this disadvantage (except leveraging the expertise of a developer), migrating to GTM will likely become inevitable. Take care of it before your business creates more pages and increases its workload for migration.
Good agencies have more than 50 testimonials.
Great agencies have more than 100 testimonials.
WebFX has over 1,100+ glowing client testimonials.
See What Makes Us Stand out

How easy is GTM for businesses to use?
Google Tag Manager is quickly becoming the standard for companies across the world.
That doesn’t mean it’s easy to use, though. In most cases, the teams that use Google Tag Manager (like marketing or advertising departments) don’t have the developer background that can make adopting and using GTM seamless.
“If you decide to use Google Tag Manager, expect a learning curve. You will need to do some reading, take some classes, and do some hands-on training to become comfortable with GTM.
It’s worth the time and effort, though.”
If you do decide to use Google Tag Manager, which you should because of its advantages, expect a learning curve. You will need to do some reading, take some classes, and do some hands-on training to become comfortable with GTM. It’s worth the time and effort, though.
Starting with the Google Tag Manager Fundamentals course from Google is an excellent first step.
Don’t miss our Marketing Manager Insider emails!
Join 200K smart marketers for the hottest marketing news and insights in your inbox.
Inline Subscription Form
“*” indicates required fields


Learn more about using GTM for your digital marketing strategy
Without a doubt, GTM comes with a learning curve. Continuing to read about it, as well as invest in some hands-on training, can help your team understand how Google Tag Manager works. With a better understanding of this free tool, you make adopting it more manageable, which lets you take advantage of all its benefits with minimal hassle.
Get helpful marketing tips and more info about using GTM with our email newsletter — Revenue Weekly. Sign up today for your free content!
-
 Sarah Berry is a Lead Web Marketing Consultant at WebFX. With more than 10,000 hours of experience, she offers practical insights and strategies you can use to grow your digital revenue. When she isn’t polishing her Time Magazine Person of the Year Award, she’s spending time with her flock of ducks.
Sarah Berry is a Lead Web Marketing Consultant at WebFX. With more than 10,000 hours of experience, she offers practical insights and strategies you can use to grow your digital revenue. When she isn’t polishing her Time Magazine Person of the Year Award, she’s spending time with her flock of ducks. -

WebFX is a full-service marketing agency with 1,100+ client reviews and a 4.9-star rating on Clutch! Find out how our expert team and revenue-accelerating tech can drive results for you! Learn more
Try our free Marketing Calculator
Craft a tailored online marketing strategy! Utilize our free Internet marketing calculator for a custom plan based on your location, reach, timeframe, and budget.
Plan Your Marketing Budget
Table of Contents
- What is Google Tag Manager?
- What is the difference between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics?
- What does Google Tag Manager do?
- 6 crucial components to GTM
- 4 advantages of Google Tag Manager
- 2 disadvantages of Google Tag Manager
- How easy is GTM for businesses to use?
- Learn more about using GTM for your digital marketing strategy

Proven Marketing Strategies

Proven Marketing Strategies
Try our free Marketing Calculator
Craft a tailored online marketing strategy! Utilize our free Internet marketing calculator for a custom plan based on your location, reach, timeframe, and budget.
Plan Your Marketing Budget
What to read next