What are the ADA compliant website requirements?
The U.S. Department of Justice hasn’t released official ADA compliance guidelines, like “maintain XYZ contrast ratio.” Its requirement is for online programs, services, and goods to be accessible to people with disabilities.
To reach that requirement, it recommends using the following standards and guidelines as a reference:
- Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
- Section 508 Standards
Keep reading to learn how to follow these resources next!
What is ADA?
ADA stands for Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), and is one of the most important accessibility laws in the U.S. because it prohibits discrimination based on disability in employment, public accommodations, transportation, and more.
Is ADA the same as Section 508?
No, ADA is not the same as Section 508, which is a federal accessibility law that applies to federal agencies and their technology, like telephones, websites, call centers, and more. Section 508, however, is recommended by the U.S. Justice Department as an ADA compliance resource.
Is ADA the same as WCAG?
ADA is not the same as WCAG, which are accessibility standards from the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The U.S. Justice Department recommends WCAG as an ADA compliance resource and is the one used most often by businesses.
Is ADA compliance mandatory?
ADA compliance is mandatory for businesses open to the public and state and local government agencies. Even if your company is exempt from ADA standards, you should consider becoming ADA compliant because it makes your website accessible to all users.
What are some examples of ADA compliance?
Some examples of ADA compliance include:
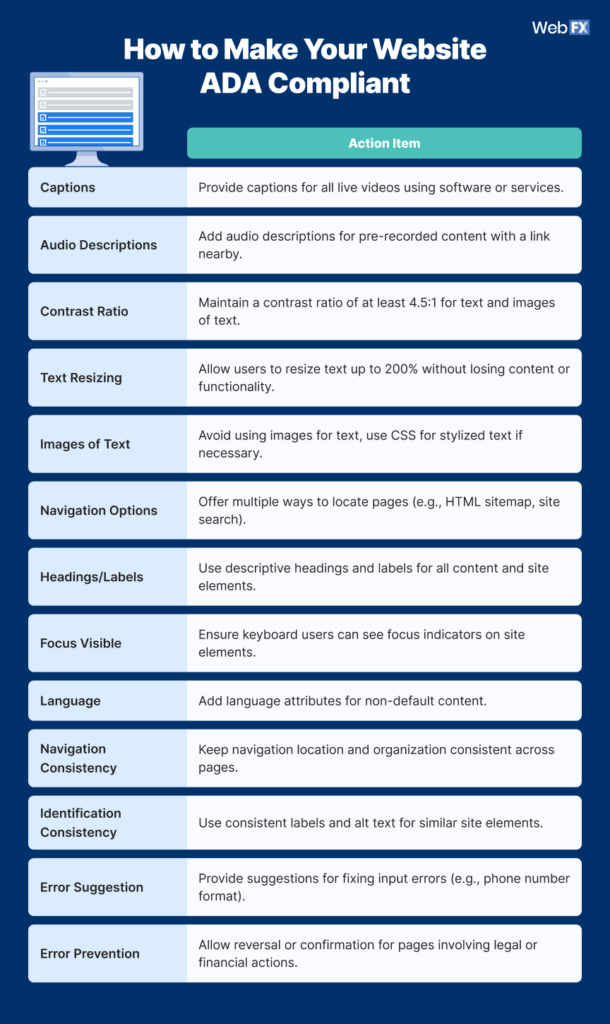
- Having video captions: Adding closed captioning to videos enables people who can’t hear your videos to still understand what’s happening in them.
- Adding image alt text: If someone is using a screen reader on your website, image alt text will provide them context as to what images are on your website.
- Allowing keyword navigation: If someone can’t physically use a mouse, allowing keyboard navigation makes it easier for these individuals to go through your website.
- Using headings to break up website content: Headings help break up text on your website and make it easy to digest.
- Use contrast ratio: Contrast ratio ensures that text is easier to read.
- Label forms: Including labels outside your form fields ensures that people see what information to provide. If you only include it in the box (with light gray text), people may have trouble reading it.
What are some examples of ADA non-compliance lawsuits?
Some examples of ADA non-compliance lawsuits include:
- Rite Aid
- Teachers Test Prep
- H&R Block
- Project Civic Access
- Louisiana Tech
- Nueces County, Texas
You can find more examples via the U.S. Department of Justice.
How much does reaching ADA compliance cost?
Costs for achieving ADA compliance vary, with ADA services typically costing $1500 to $5000. How much your business pays will depend on your website’s size, current compliance, timeline, service provider, and other factors.
Where can I learn more about becoming ADA compliant?
You can learn more about becoming ADA compliant with these resources:
What’s considred a violation of ADA?
A violation of ADA is anytime a business fails to provide reasonable accommodations for people with disabilities. In terms of your website, you can violate ADA by neglecting to make your website compliant.