-
 Published: Aug 9, 2023
Published: Aug 9, 2023
-
 10 min. read
10 min. read
-
 Savannah Swanson
Savannah Swanson Lead Digital & Social Trends Writer
Lead Digital & Social Trends Writer
- Savannah is a content marketer with editorial experience spanning several businesses. Specializing in social media and marketing trends, she loves talking about the latest developments in online marketing. When she’s not writing, Savannah loves traveling, hoarding books and coffee mugs, and adoring her cat. Please don’t ask her about famous true crime cases, or else she’ll tell you all about her theories and get absolutely no work done.
Search engine optimization (SEO) wasn’t always the way it is now, with logical keyword usage and an emphasis on answering search intent. In fact, early SEO used to be much different (and chaotic).
Today we’re looking at the evolution of SEO, from chaos and confusion to clearer guidelines, ethical optimization tactics, and order (with a bit of chaos every now and again). Keep reading to learn more about the history of SEO and the changes it’s undergone to get to where it is today with this comprehensive timeline of major SEO milestones.
- Early SEO: 1990s
- “Powered by Google”: 2000 — 2005
- Improving search results: 2006 — 2010
- SEO as we know it: 2011 — now
Looking to expand your knowledge of SEO even more? WebFX is an award-winning SEO agency with over 29 years of experience. Learn how you can do more with your SEO by checking out our SEO services today or giving us a call at 888-601-5359.
We’re masters of our craft.


300+

9,000+

4,000+

200+

100+
Early SEO: 1990s
SEO evolution begins in the early 1900s, or as we like to call it, the wild west of the Internet. As more and more websites began to populate the Internet, major players like Yahoo and Google emerged to improve website cataloging.
During this time, SEO was in its infancy and early search engines were dictated by black-hat SEO tactics like keyword stuffing and excessive backlinking (which were usually spammy).
From the first website to Google’s grand entrance, here’s how SEO began and the major advancements in saw in the 1990s.
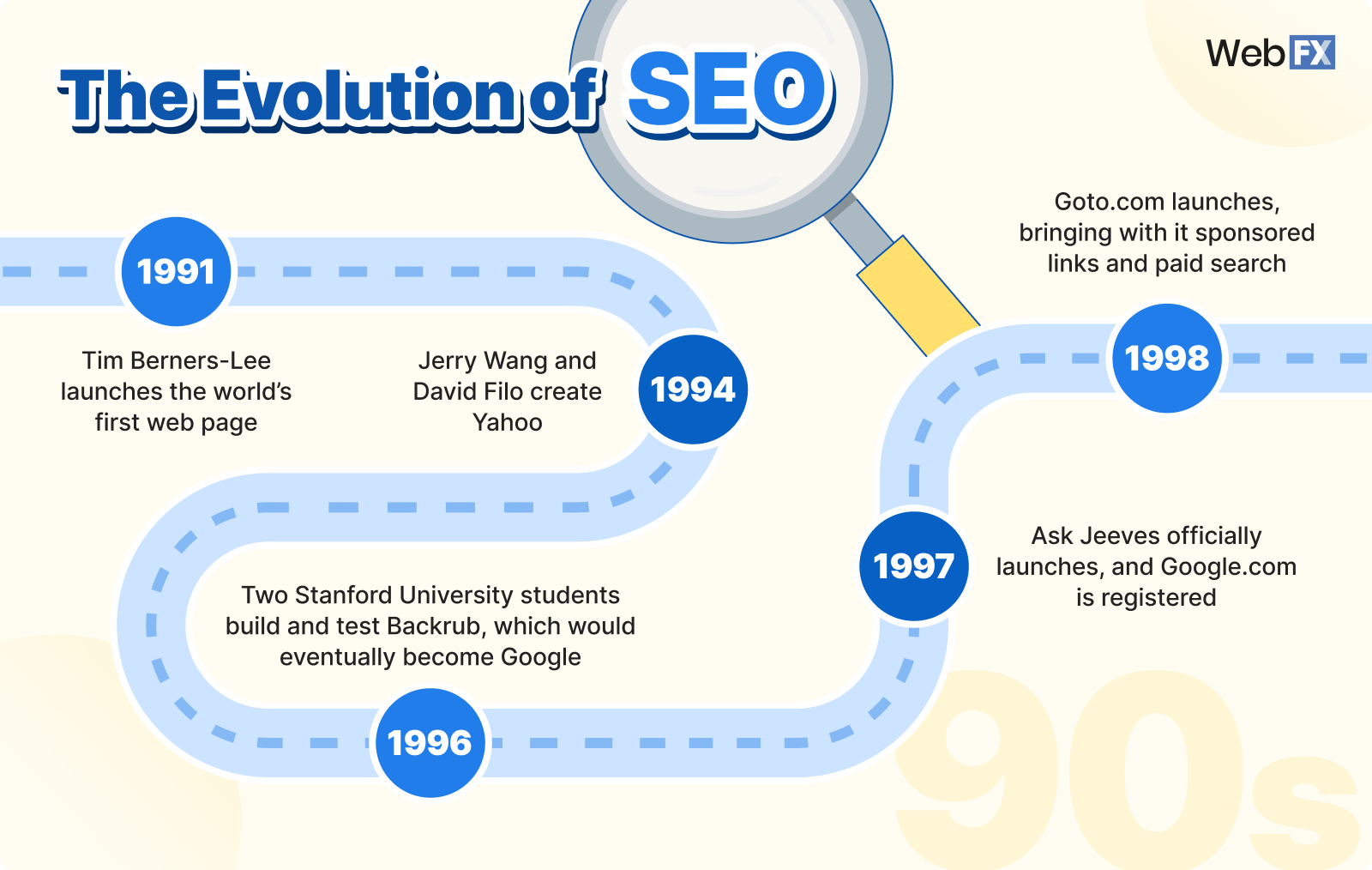
1991
Tim Berners-Lee launches the world’s first web page at the web address info.cern.ch.
Dedicated to information about the World Wide Web Project, Berners-Lee’s website ran on a NeXT computer at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN).
1994
Stanford University students Jerry Wang and David Filo create Yahoo in a campus trailer.
Originally, Yahoo served as an Internet directory and bookmark list, and webmasters had to manually submit their pages for indexing to the Yahoo directory.
At this time, AltaVista, Excite, Lycos, and Infoseek also launched.
1996
Two Stanford University students build and test Backrub, a search engine that ranks pages based on the number of backlinks pages have and how trustworthy the linking sites are.
Backrub would eventually become Google, the search engine we know and love today.
Additionally, 1996 saw the founding of AskJeeves.com, later known as Ask.com, a natural language search engine that ranked sites by popularity. This method made it very easy to spam search engines.
HotBot, powered by Inktomi, a Yahoo company, also launched.
1997
Ask Jeeves officially launches, and Google.com is registered.
1998
Goto.com launches, bringing with it sponsored links and paid search.
Powered by Inktomi, Goto.com, later known as Overture, was the first search service company to provide pay-per-click (PPC) placement for links.
“Powered by Google”: 2000 — 2005
Welcome, Y2K! As a new millennium emerged, so did a new kingpin in search engines and SEO. Enter the Google revolution.
The early 2000s era of SEO saw a dramatic shift in ranking factors. Leaving unethical optimization tactics in the rearview, Google built the foundation for more regulated search results that prioritized ethical practices like valuable and relevant content.
This period in the history of SEO focused on creating better search experiences that were user focused. Look at how Google revamped search engines with early 2000s SEO.
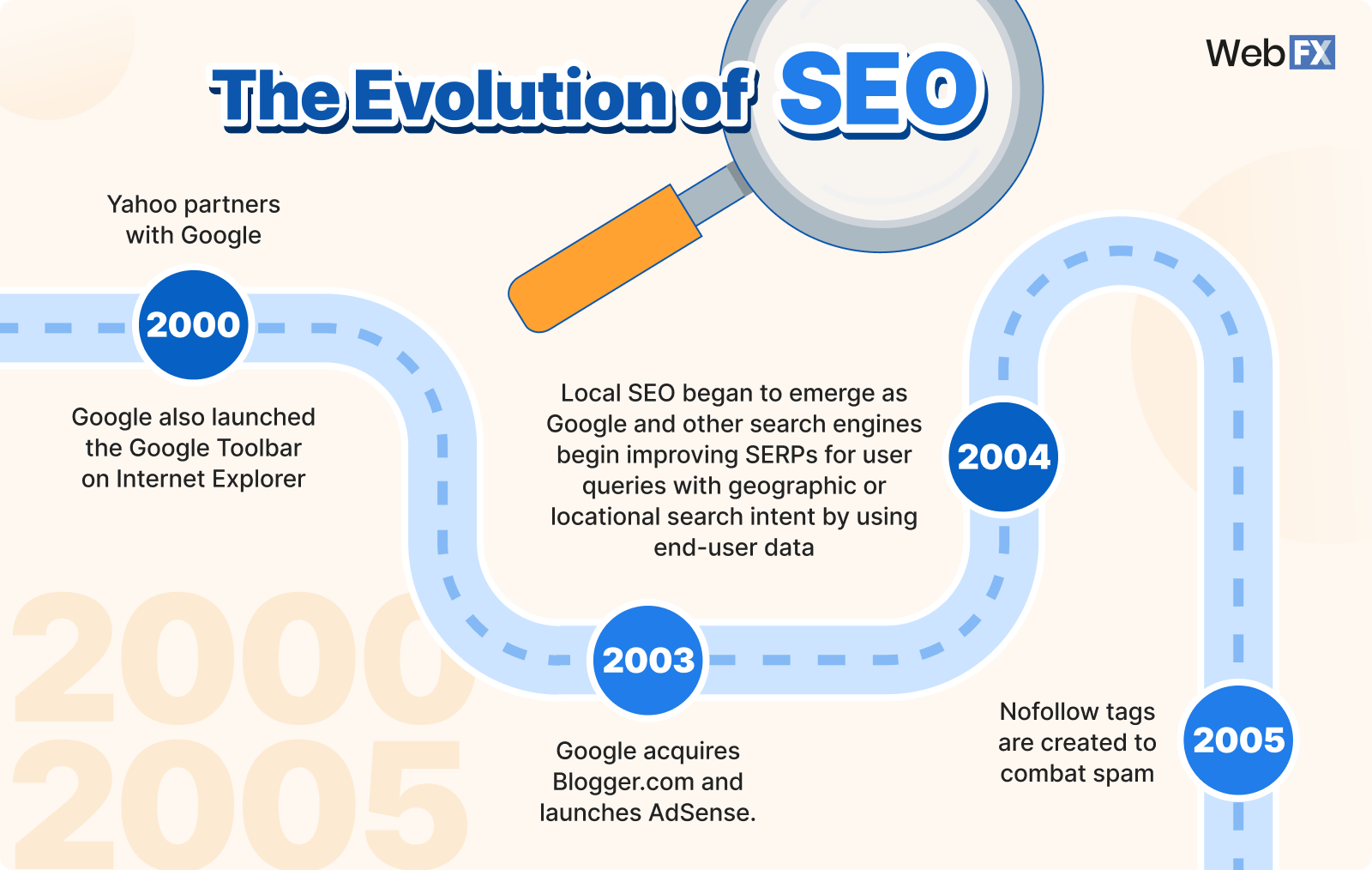
2000
Yahoo partners with Google, which was a little-known search engine at the time.
With this partnership, Google began powering Yahoo’s organic search results instead of Inktomi. As a result, every Yahoo search result said “Powered by Google.”
Expanding the range of its ranking factors, Google starting looking at on-page and off-page SEO factors when ranking content for search engine results pages (SERPs). Most notably, Google looked at the quality and quantity of external links to a website, as well as the anchor text used.
Link building gained steam as major factor in SEO, and it started to become an abused tactic.
Google also launched the Google Toolbar on Internet Explorer, allowing SEO specialists to see their PageRank score.
AdWords also made its way onto the search engine scene, with their paid search ads appearing right above, below, and next to Google’s organic, unpaid search results.
2003
Google acquires Blogger.com and launches AdSense.
Adsense offered targeted ads on publisher sites, but this caused a significant surge in monetized online publishing. Unethical SEO tactics emerged, like sites with low-quality content that existed for the sole purpose of getting clicks and making money.
2004
Google and other search engines begin improving SERPs for user queries with geographic or locational search intent by using end-user data.
In other words, local SEO began to emerge, with Google using data like search history and interests to personalize search results and show better, relevant content, especially when it came to geographic searches like “pizza shops near [location]” or “restaurants near me.”
2005
Nofollow tags are created to combat spam, and Google releases two major updates to its algorithm:
- Jagger: Helped to curb the number of unsolicited link exchanges, target unnatural link building practices, and other technical SEO factors.
- Big Daddy: Improved Google’s infrastructure, impacting the quality of SERPs by allowing for a better understanding of the relationship of links between sites.
Improving search results: 2006 — 2010
In SEO evolution, the late 2000s was a bit of a whirlwind, with Google making many significant moves to improve user experience on search engines and better hone the search algorithm to show people more of what they want.
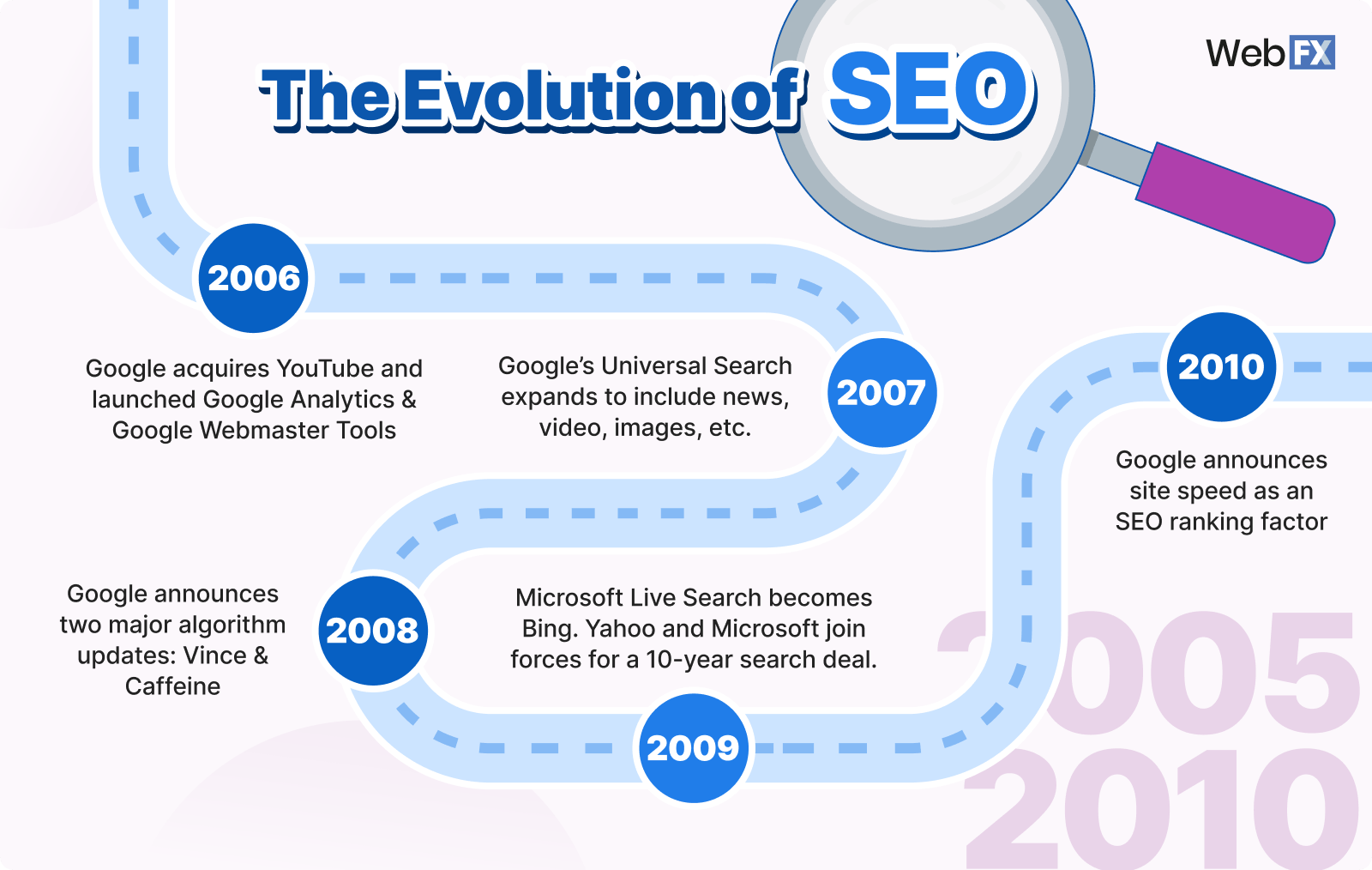
2006
Google acquires YouTube, another widely used search property, for $1.65 billion.
Along with acquiring YouTube, Google also launch two major search tools:
- Google Analytics: Helps marketers and business owners track and report on website traffic
- Google Webmaster Tools (now Search Console): Lets webmasters view crawling errors and identify searches their site shows up for.
2007
Google’s Universal Search expands and improves the search experience, including news, video, images, and other types of relevant content with organic search results.
2008
Google announces two major algorithm updates:
- Vince: Unintentionally awarded big brands in the SERPs
- Caffeine: Improved the speed of the algorithm’s indexing
2009
Microsoft Live Search becomes Bing. Plus, Yahoo and Microsoft join forces for a 10-year search deal.
This major partnership was aimed at taking on Google’s impressive grip on the search market, with Bing powering Yahoo’s organic and paid search results. Ultimately though, the partnership was no match for Google.
2010
Google announces site speed as an SEO ranking factor.
SEO as we know it: 2011 — now
Here’s where our history of SEO reaches the present. After 2010, SEO and Google’s search algorithm undergoes crucial updates that shape it into the complex (and still ever-changing) entity that it is today.
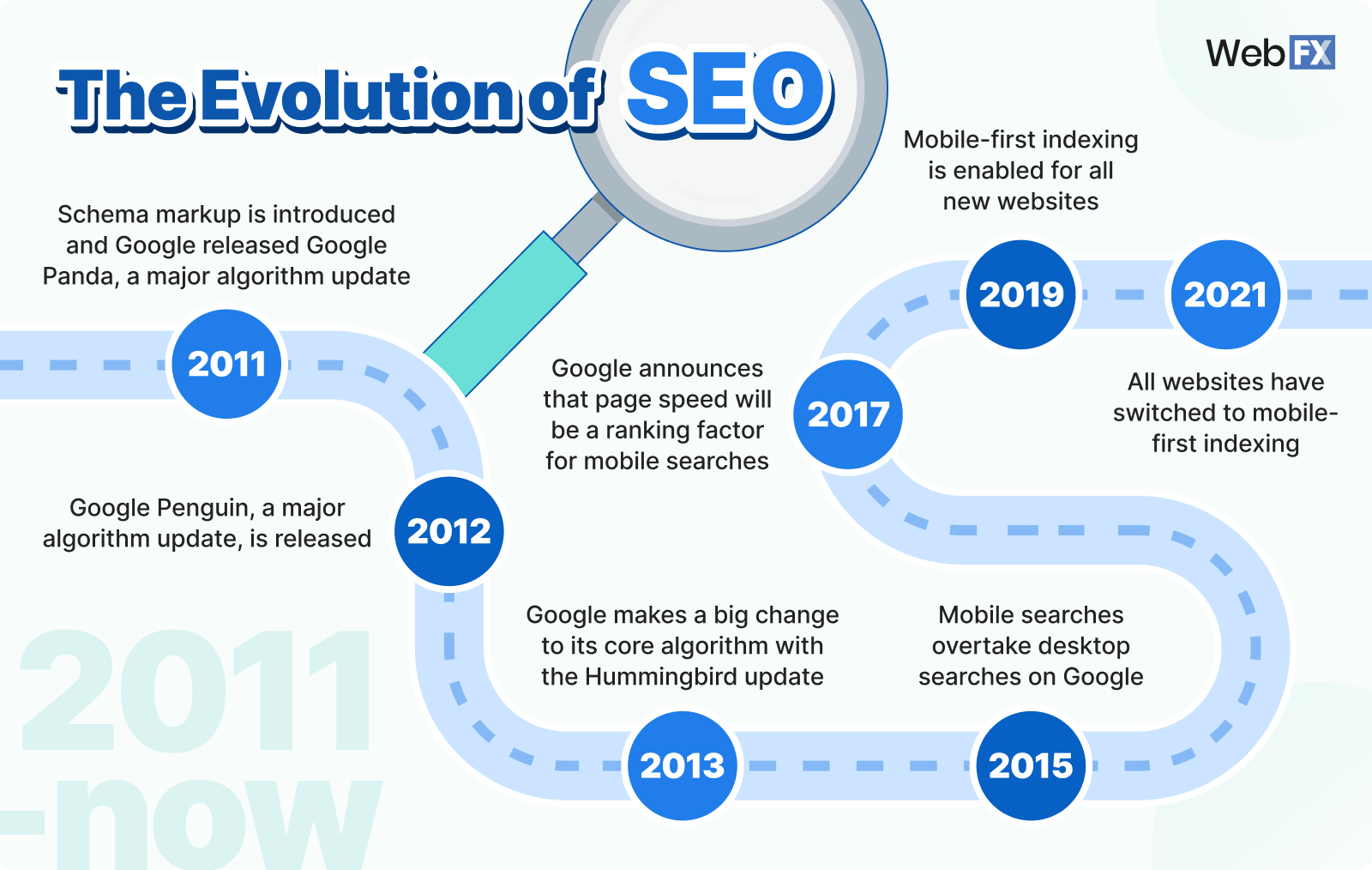
2011
Schema markup is introduced.
Schema markup is coding that allows you to optimize your site so search engines can read it better and provide more informative search results for users. While schema isn’t a ranking factor, it does help sites stand out on SERPs.
Google also released another major algorithm update, Google Panda.
Panda was aimed at weeding out thin, or low-quality content. At the time, SERPs were constantly featuring unoriginal sites filled with thin content that was, at times, outranking quality sites.
2012
Google Penguin, a major algorithm update, is released.
While Panda targeted thin content, Penguin went after spam tactics like keyword stuffing and websites with unusual link makeup.
2013
Google makes a big change to its core algorithm with the Hummingbird update.
Google Hummingbird was meant to make the SEO algorithm more precise and faster. It was also meant to better interpret natural language to understand search intent and show more relevant search results to users. This was especially important as voice search capabilities became more common on mobile devices.
2015
Mobile searches overtake desktop searches on Google, prompting the search engine to place more emphasis on mobile-friendly SEO algorithm updates.
2017
Google announces that page speed will now be a ranking factor for mobile searches.
2019 & 2021
Mobile-first indexing is enabled for all new websites in 2019, and by 2021 all websites have switched to mobile-first indexing.
SEO algorithm updates
As you can tell from this timeline, the evolution of SEO extends across decades. This brief history of SEO is just a taste of SEO’s greatest hits and major milestones. If you want to learn more about the major SEO algorithm updates implemented over the years, you can check out our timeline of Google updates below:
A Timeline of Google Algorithm Updates
Evolution of SEO: What now?
The evolution of SEO is only just beginning — with new advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, there will no doubt be future SEO algorithm updates aimed at combating duplicate and unoriginal content.
How do I keep up with the evolution of SEO?
Google makes thousands of algorithm updates every year, ranging from small changes to major core updates.
Don’t worry, the success of your website’s SEO performance isn’t dependent on knowing every one of these updates. Rather, it’s important to stay in tune with Google’s more significant algorithm changes.
Below are a few simple ways you can stay on top of the evolution of SEO and core updates:
- Monitor your site’s analytics: Many times, major changes in your site’s analytics can indicate an algorithm update. If you notice a significant change in your site’s rankings, do some digging to see if any updates were made to Google’s algorithm.
- Check social media: Even search engines are on social media — check out @searchliason on Twitter, where you can stay up to date on algorithm changes straight from Google.
- Use algorithm trackers: Algorithm trackers like Moz’s MozCast or SEMrush’s Sensor can help you track algorithm changes that directly affect your website’s performance and metrics.
- Partner with an SEO agency: SEO agencies live and breathe the SEO algorithm and everything that comes with it. When you work with an agency, you can rest assured knowing you’ll always have someone keeping an eye on changes with the SEO algorithm and helping you successfully navigate them.
Clutch has personally interviewed more than 250 WebFX clients to discuss their experience partnering with us.Independent research from Clutch has named WebFX the
top SEO company in the United States.


Stay on top of SEO with an award-winning SEO agency
Did you know WebFX is an award-winning SEO agency with 395+ Clutch reviews and 300+ Google-certified team members? With over 29 years of experience, we’ve had a front row seat to the evolution of SEO and know how to help businesses keep up with them.
Give WebFX a call at 888-601-5359 to learn more about our SEO services, or contact us online today to learn more about how you can improve your search engine visibility with WebFX today.
-
 Savannah is a content marketer with editorial experience spanning several businesses. Specializing in social media and marketing trends, she loves talking about the latest developments in online marketing. When she’s not writing, Savannah loves traveling, hoarding books and coffee mugs, and adoring her cat. Please don’t ask her about famous true crime cases, or else she’ll tell you all about her theories and get absolutely no work done.
Savannah is a content marketer with editorial experience spanning several businesses. Specializing in social media and marketing trends, she loves talking about the latest developments in online marketing. When she’s not writing, Savannah loves traveling, hoarding books and coffee mugs, and adoring her cat. Please don’t ask her about famous true crime cases, or else she’ll tell you all about her theories and get absolutely no work done. -

WebFX is a full-service marketing agency with 1,100+ client reviews and a 4.9-star rating on Clutch! Find out how our expert team and revenue-accelerating tech can drive results for you! Learn more
Try our free Marketing Calculator
Craft a tailored online marketing strategy! Utilize our free Internet marketing calculator for a custom plan based on your location, reach, timeframe, and budget.
Plan Your Marketing Budget

SEO Success with KOA

Proven Marketing Strategies
Try our free Marketing Calculator
Craft a tailored online marketing strategy! Utilize our free Internet marketing calculator for a custom plan based on your location, reach, timeframe, and budget.
Plan Your Marketing Budget
What to read next