- Home
- Blog
- Web Design How to Find and Remove Broken Links in Your Website
How to Find and Remove Broken Links in Your Website
-
 6 min. read
6 min. read
-
 William Craig
William Craig CEO & Co-Founder
CEO & Co-Founder
- President of WebFX. Bill has over 25 years of experience in the Internet marketing industry specializing in SEO, UX, information architecture, marketing automation and more. William’s background in scientific computing and education from Shippensburg and MIT provided the foundation for MarketingCloudFX and other key research and development projects at WebFX.
Broken links are links that lead to pages that do not exist. When clicking on a broken link, the page you land on is called a 404 error page. What does 404 mean? A 404 not found error page is a standard HTTP response that indicates that the requested URL doesn’t exist.
What do you do when you happily surf the web and suddenly come across a 404 error? For most of us, the immediate response would be to simply leave the current site in favor of another one because both people and search engines consider broken links as unprofessional. 404 errors and broken links also have negative effects on your search engine rankings so it is quite reasonable to be proactive in avoiding them to improve exposure and increase site traffic.
Note: there are terms and methods presented in this tutorial that address WordPress bloggers, however, this article is relevant to any website owner.
Bloggers update their blog’s content more often than other site owners do. Therefore, there is a higher chance for them to have broken links found throughout their website. For WordPress blogs, there are two types of plugins that can be used to deal with those links:
- Plugins that detect broken links in your site like Broken Links Checker.
- Plugins that manage 301 redirects automatically like Redirection.
As a plugin minimalist, I always insist on doing things manually to avoid using and installing plugins. In this case, you can rest assured that having the ability to deal with these problems efficiently is worth installing another plugin. (See the short list of plugins that Six Revisions uses.) Whether you use a plugin or not, I highly recommend checking your website occasionally for broken links and 404 errors.
Detecting and removing invalid URLs using Google WebMaster Tools
There are two reasons why pages are indexed in Google even though they don’t exist on your website:
- You referenced an invalid internal link by mistake because of a typo. This is the time to recommend a very simple yet essential plugin for post authors – the Link to Post plugin for avoiding such mistakes).
- You published a post and decided to change its permalink afterward (the post’s SEO slug) after Google has already indexed the original link.
The best way to detect these errors is by using Google Webmaster Tools. If you haven’t done so already, register your site there. It’s an essential tool to have for anyone running a website.
One of the most important tools provided in GWT is the Remove URL tool, which allows you to remove invalid pages from Google search results. Let’s see how to remove those bad URLs from Google’s index.
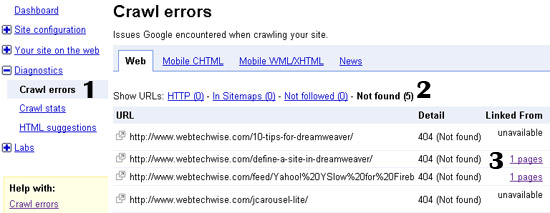
Detecting invalid pages that are indexed by Google
Once you have signed up for Google Webmaster Tools and have set it up and verified your site (see Google’s Getting Started guide for GWT), here is the process for finding invalid pages.
- Click on Diagnostics from the left menu and select Crawl Errors.
- Select the Not Found category.
- If available, click to view which page contains the broken link.
- To make sure that the URL is indeed indexed in Google, copy and paste the URL into Google’s search and see if any result comes up.
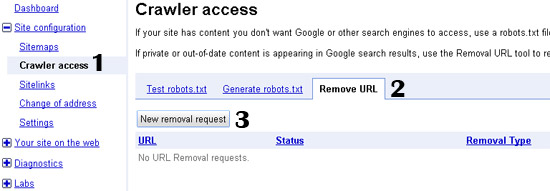
Removing URLs from Google’s search results
- Click on Site Configuration, and select Crawl Access.
- Select Remove URL.
- Click on New removal request.
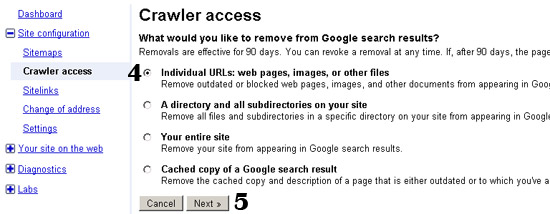
4. Select the first option to completely remove a page from Google search results. OR Select the fourth option in case you want to retain the page in search results but would like to remove the cached version of the page. This is useful in case Google displays an outdated version of the page in the “cached” link.
5. Click on Next.
6. Type the URL of the page you would like to remove from Google.
7. Make sure the first option is selected and then click on Add.
8. The URL to be removed should now appear in the list. If you want, you can add more pages for removal.
9. Click on Submit Removal Request. 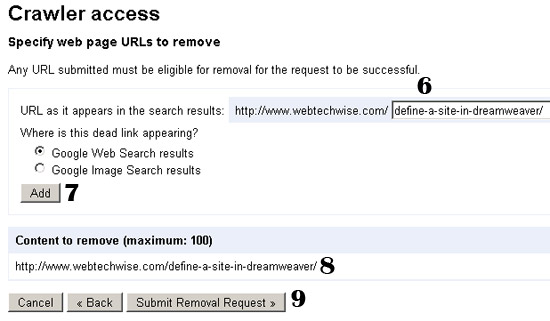
Your request is now pending—in most cases, it only takes 2 to 3 days for Google to remove the URL.
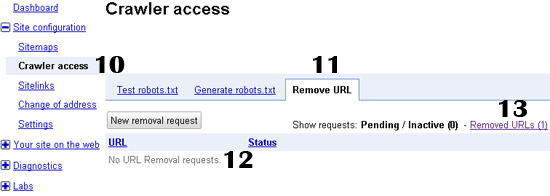
10. Click on Site Configuration and select Crawl Access.
11. Select Remove URL.
12. Make sure the URL you requested to remove does not appear in the list of pending requests.
13. Click on Removed URLs to see that the URL is now listed there. To make sure that the URL was indeed removed from Google, copy and paste the URL into Google’s search box and see if any result comes up.
Detecting broken links using Xenu Link Sleuth
Another excellent tool I like using for hunting down broken links in my websites is Xenu Link Sleuth. You can download it here.
Unlike the WordPress plugins mentioned earlier in this article, Xenu is a standalone desktop application for Windows that outputs all your site links—whether they’re valid or invalid links—and groups them into a very readable fashion. 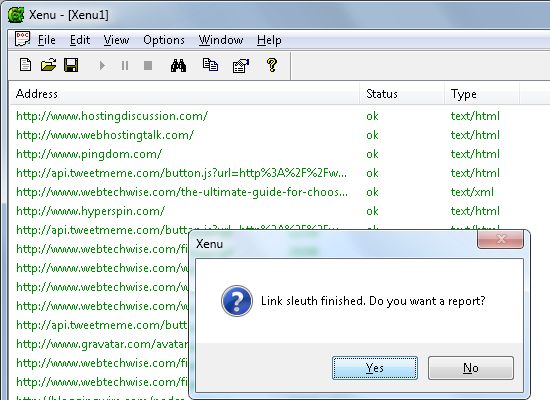
After you install Xenu, using it is really easy.
- Click on File and select Check URL.
- Type your website’s URL (e.g. https://www.webfx.com/blog/web-design/.
- Wait for all links (site wide!) to be checked.
- When Xenu asks whether you want a report, click on Yes.
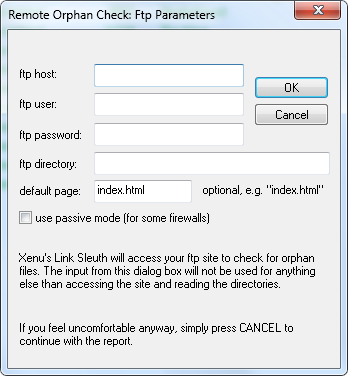
You can enter your FTP server details, but I simply click on Cancel and Xenu generates an XHTML report locally (it opens a dialog window automatically). In the generated report, click on Broken links.
Sort it by link in the table of contents to see all the pages that have broken links in them (and the broken links of course).
Finally, once you’ve detected all broken links, what is left to do is to navigate to the posts and pages containing references to broken links. You should either fix or remove those links.
What are your own techniques and tools for finding broken links?
How often do you search your site for broken links? How important is it to eliminate invalid links, and why?
Related content
-
 President of WebFX. Bill has over 25 years of experience in the Internet marketing industry specializing in SEO, UX, information architecture, marketing automation and more. William’s background in scientific computing and education from Shippensburg and MIT provided the foundation for MarketingCloudFX and other key research and development projects at WebFX.
President of WebFX. Bill has over 25 years of experience in the Internet marketing industry specializing in SEO, UX, information architecture, marketing automation and more. William’s background in scientific computing and education from Shippensburg and MIT provided the foundation for MarketingCloudFX and other key research and development projects at WebFX. -

WebFX is a full-service marketing agency with 1,100+ client reviews and a 4.9-star rating on Clutch! Find out how our expert team and revenue-accelerating tech can drive results for you! Learn more
Make estimating web design costs easy
Website design costs can be tricky to nail down. Get an instant estimate for a custom web design with our free website design cost calculator!
Try Our Free Web Design Cost Calculator

Web Design Calculator
Use our free tool to get a free, instant quote in under 60 seconds.
View Web Design CalculatorMake estimating web design costs easy
Website design costs can be tricky to nail down. Get an instant estimate for a custom web design with our free website design cost calculator!
Try Our Free Web Design Cost Calculator