2025 Beginner’s Glossary of PPC Terms
What is CPC?
GlossaryWhat Is Cost Per Click (CPC)? Launch Your CPC Campaign Cost per click (CPC) is a paid advertising metric that measures how much an advertiser pays for every click on their pay-per-click (PPC) ads. You can calculate CPC with a […]
What is PPC?
GlossaryWhat is PPC? The All-Encompassing PPC Guide With pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, you can quickly increase your visibility online and target ads to your ideal prospects. Plus, you only pay when someone clicks on your ad, which helps you get an […]
What is B2C PPC Advertising?
GlossaryWhat Is B2C PPC Advertising and How Does It Work? Advertising is critical for any business, and the Internet is a fantastic place to do it. By displaying paid ads online, you can reach large audiences of people in multiple […]
What is SMB PPC Advertising?
GlossaryWhat Is SMB PPC Advertising and How Can It Benefit Your SMB? SMB PPC advertising, also called small-to-midsized business (SMB) pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, is the process of promoting a SMB on digital ad networks that use a pay-per-click payment model, […]
What Are Negative Keywords
GlossaryWhat Are Negative Keywords? Pay-per-click advertising (PPC) is one of the most valuable marketing opportunities for companies in all industries. It lets you reach new customers for only pennies per ad, and you don’t even pay for an ad unless […]
What Are Google Ad Grants
GlossaryWhat are Google Ad Grants? The Google Ad Grants program allows nonprofit organizations to advertise on Google AdWords cost-free. Eligible nonprofits are allotted a $10,000/month AdWords budget to promote themselves and advance their missions. View our Digital Services
And once you get them up, they’ll start showing results instantly, meaning revenue in your pocket. With this convenient PPC glossary in hand, you’ll be ready to tackle any PPC campaign.
Check out these PPC trends for 2025
But, what’s pay-per-click advertising (PPC)?
PPC’s definition refers to paid ads that appear at the top of search engine results pages (SERPs) — above organic results — and on sites across the web. In search results, PPC ads usually include green [Ad] indicators, so searchers know they’re viewing paid content.
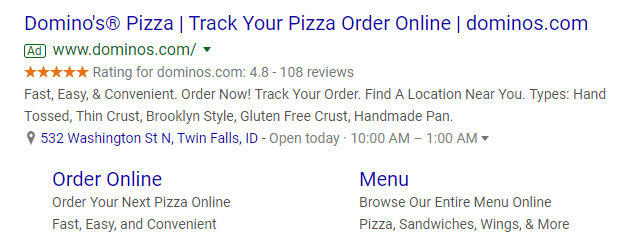
Learn more: How Long Does it Take PPC to Work?
Why is PPC important?
The wonderful thing about PPC is that when you create a PPC ad, you only have to pay when a user clicks the ad’s link to your landing page, making it the most cost-effective advertising method out there. Better yet, the results are instant!
Are you just getting into researching PPC ads for your next advertising campaign? This beginner’s glossary of commonly used PPC terms will help you understand what all those crazy acronyms mean. Even if you’re a seasoned PPC expert, you may find some hidden gems to add to your next campaign.
The PPC terminology is sorted alphabetically. To find a specific PPC term and its definition, click one of the letters below to jump to a section, or keep scrolling until you find the term you’re looking for. Just keep reading for your comprehensive PPC glossary!
If you want to know more about campaign definitions, speak with a PPC expert before reading on? Contact us online or call us at 888-601-5359 to get your next campaign rolling!
Check all PPC terms your need to know in 2025 right here
A
Active view cost-per-thousand impressions (active wiew CPM):
A bidding type where you bid for 1000 viewable impressions, meaning you only pay for the impressions where at least 50% of the ad is on-screen for no less than one second.
Ad campaign:
Set of advertisements that share the same concept, theme, and goal. The campaign can have one or multiple ad groups, meaning that the PPC ads in the ad groups and the whole ad campaign will generally target related keywords.
Ad copy:
Refers to any text that occurs with an ad. For PPC, this generally indicates the headline, any descriptions, and the URL. The best ad copy engages the viewer.
Ad delivery:
Setting in Google Ads that paces the delivery of your ad throughout the periods of times that you set or throughout the day.
Ad extensions:
Google Ads features that allow additional pieces of information, like price, extra links, ratings, etc., you can add free of charge to your pay-per-click ad. If a user clicks on the additional information, you will be charged the same as when they click on your PPC ad’s main link.
Ad group:
Set of ads that target related keywords generally under one bid. Ad groups are used to keep your account and campaign organized.
Ad network:
Any company that specializes in serving as brokers between advertisers and websites wanting to host ads.
Ad position:
The position that your advertisements show in the search engine results pages (SERPs). There are, on average, ten paid ad positions on each page. Usually, the first ad on the search page, ad position “one,” earns the most clicks.
Ad rank:
The value that is used to determine your ad position in the SERPs and is calculated by the amount you bid multiplied by your ad keyword’s quality score.
Ad rotation:
Google Ads setting that allows you to rotate the set of ads within your ad group automatically every time the SERP is refreshed. You can either rotate your ads evenly or have Google select the best performing ads to rotate.
AdSense:
Google program that compensates sites for showing paid ads. AdSense works by matching relevant text and display ads to the content and visitor demographics on the hosting sites.
Ad scheduling:
Also called “dayparting.” It allows you to customize the periods that your ads run so that you can target times of the day in which your ad would be more successful.
Ad Status:
Description from Google marking whether your ad is eligible to run, as well as any restrictions on how or where it runs.
Advertising policies:
Guidelines from advertising platforms for your advertising campaign, which can include requirements for your ads, keywords, or site. If your ads violate the platform’s policies, they won’t run.
Amazon advertising:
Amazon’s advertising platform for advertising on product pages as product display ads, banner ads, or suggested searches.
Assisted conversion:
Measure of the interaction of users leading up to conversion, but not the last click to convert on your site. The value allows you to see which channels perform the best in your multi-channel advertising campaign.
Audience:
Group of users with predefined demographics that you want to convert with your advertising campaign. It can also refer to the users who have completed specific actions such as visiting your website or shown interest in your services.
Automated Extensions:
Set of Google Ads features that automatically generate information snippets for your paid ad.
Automated Rules:
Google Ads feature that will make automatic adjustments to your ad campaign based on customizations, such as seasonal factors, that you set in place beforehand.
Automatic Bidding:
Google Ads places your bid amount for you to gather the highest amount of clicks possible while staying within your budget. Your bid will automatically go up by the amount you specify after a competitor bids for the same keyword.
Auto-tagging:
Google Ads feature that automatically tags your destination URLs with Google Click Identifiers (GCLID) that help track your ad performance with Google Analytics.
Average Cost-Per-Click (Avg. CPC):
Average amount of money spent when users click on your ad’s landing page.
B
B2C PPC
Business-to-client PPC is a method of digital advertising involving running pay-per-click campaigns to target individual customers or online consumers.
Bid:
Also called “Keyword Bid.” The maximum price you want to spend for clicks for keywords that your target with your paid ads.
Bidding types:
Four ways to bid for your target keywords and their ad space include: Cost-per-click (CPC), cost-per-thousand impressions (CPM), Active View cost-per-thousand impressions (Active View CPM), and cost-per-engagement (CPE). Advertisers choose which method best suits their advertising goals.
Bid management:
Regulating bids to obtain the minimum bid for a keyword by grouping and optimizing keywords. Google has features that will allow you to do this automatically. Otherwise, you can do this manually or outsource to a bid management agency like WebFX.
Bounce:
A single-page session on your site where users click to your page, then leave before they view any other pages on your site.
Bounce rate:
Ratio of users who bounce after visiting your page.
Broad match:
Default keyword matching options for ads. It allows you to show your ad when the search query contains your keyword in any order or contains any misspellings, synonyms, related searches, or relevant variations.
C
Call extensions:
Also called “Click-to-Call.” Google Ads feature that allows you to add your business phone number beneath the text of your PPC ad, which will enable users to click the number to place a call.
Callout extensions:
Google Ads feature that you can use to promote offers such as free shipping, price matching, or 24-hour service beneath your ad’s text.
Call-To-Action (CTA):
Any action you encourage your visitors to take, such as calling in, signing up for email newsletters, or buying a product. For PPC, this means clicking on your ad’s link and heading to your landing page (which can have additional CTAs).
Change history:
Google Ads tool that allows you to view all changes from a specific date range with filter options for particular changes, such as bid adjustments, status changes, and keyword additions.
Click:
The action of following a link to a website. For PPC, this is precisely how many people click on the link to your landing page.
Click fraud:
Clicks for PPC ads made with malicious intent.
Click-Through Rate (CTR):
Ratio of the number of clicks against the number of times the ad was shown (impressions). It’s used to help you measure your advertising campaign’s performance.
Client ID:
The 10-digit string of numbers assigned to each browser or device in the Google system.
Conversion:
Any action you want your visitor to take that you deem is valuable, such as calling, filling in a form, signing up for a newsletter, or purchasing a product or service. For a PPC campaign, generating more of a specific type of conversion is often the goal.
Conversion optimizer:
Google Ads feature that helps adjust your bids depending on which clicks will likely be profitable.
Conversion rate:
atio of the number of conversions divided by the number of clicks. It helps you determine how successful your ad campaign is by determining how often a click becomes a conversion.
Cookies:
Small files used to track user preferences and search history. It helps search engines track conversions and returning visitors.
Cost-Per-Click (CPC):
Cost-per-click (CPC) is a digital advertising bidding model in which advertisers pay every time a user clicks on their ad. Cost per click is a crucial metric to consider when running things like PPC ad campaigns.
Cost-Per-Conversion:
The average cost required for a conversion on your site.
Cost-Per-Engagement:
The average cost for any time a user interacts with your ad in some manner.
Cost-Per-Impression (CPI):
The average cost per ad shown in the search pages and an alternate bidding option to cost-per-click.
Cost-Per-Lead (CPL):
The average cost it takes to generate a lead.
Cost-Per-Acquisition (CPA):
The average cost it takes to generate a customer.
Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions (CPM):
Maximum price you are willing to bid for every thousand impressions you receive.
Cost-Per-View (CPV):
The average cost per view on a video ad.
Customer lifetime value (CLV):
Estimate of how much profit a customer will generate over the course of an entire relationship with your business.
D
Daily budget:
Amount of money you choose to be spent each day for your ad campaign.
Destination URL:
The URL of your landing page.
Display network:
Also called “Content Network.” A network of partnered sites and apps where it’s possible to show your ad if you agree to pay a part of the ad’s revenue.
Display URL:
The URL shown with your PPC ad. This can be your destination URL or a separate, shorter URL. Only have one display URL for each ad group with the same root domain as your destination URL.
Dynamic keyword insertion (DKI):
Google Ads feature that allows you to dynamically insert the keywords users search in place of a string of code directly into your ad copy and bold it so that it’s more noticeable to searchers.
E
Effective Cost-Per-Click (eCPC):
Also called “Estimated Cost-Per-Click.” The ratio of total earnings against total clicks. It helps you measure the cost-effectiveness of the clicks you gained in your campaign.
Enhanced Cost-Per-Click (ECPC):
Google Ad feature that provides automatic bid management for your manual bids. It raises and lowers your custom bids for keywords predicted to be more or less likely to convert, increasing the ROI for your ad campaign.
Exact match:
Allows you to specify whether to show ads only if the search query matches your keyword word-for-word.
Expanded text ad:
Contains two 30-character headings and an optional third heading, as well as two 90-character description fields, which increases the amount of text you can include in your ads.
F
Facebook ads:
Facebook’s advertising platform that allows you to use the demographic data gathered by Facebook to target any group you specify with personalized ads.
Facebook dynamic ads:
Automatically generated ads from an uploaded product catalog that directly target users who previously exhibited interest in your brand anywhere on the web.
Free clicks:
Interaction with your interactive ad that results in clicks, which require no payment from you.
Frequency capping:
Google Ads feature that allows you to restrict the number of times a specific user will see your ad over a set period.
G
Geofencing:
Targeting a specific geographic radius (at least one mile) by drawing a virtual fence and using GPS to track user data and show your ads to users located within that area. It’s considered more accurate than geotargeting.
Geotargeting:
Also called “Location Targeting.” Limiting your advertisements to a broader geographical region than geofencing and to demographic criteria such as age range.
Google ads:
Originally “Google AdWords.” Google’s online advertising platform that helps advertisers manage and maximize the performance of their advertising campaigns.
Google ads application programming interface (API):
Allows developers to create applications that interact directly with their Google Ads account to simplify the management of complex ad campaigns.
Google Ad Grants allow non-profit organizations to advertise on Google Ads free of charge. Qualifying non-profits are provided $10,000/month to create text-based ads and create effective campaigns.
Google Optimize:
Google’s website testing and optimization platform. It allows the user to conduct tests on their landing pages against variant pages to make incremental improvements to their site’s performance.
H
Headline:
First line of your PPC ad. It contains a maximum of 25 characters and is what users notice first.
Head terms:
Also called “head keywords,” or “short tail keywords”. Short, high-volume, highly competitive keywords, such as “pizza,” that are generally broad in meaning. For PPC, head terms are more costly to bid for than lower volume, less competitive keywords.
Hits:
Amount of views a webpage has. The number includes both new and returning visitors and helps you determine how effective your click-through-rate is for your PPC ad.
I
Image ads:
Ads with graphics providing information about your product.
Impression:
The total number of times your ad is shown in a SERP or a Google Network site.
Impression share (IS):
Ratio of the number of impressions you received against the estimated number of impressions you could have received.
Instagram ads:
Instagram’s advertising platform that allows you to create video or photo ads for your audience on Instagram.
Interest categories:
Google Ads setting that allows you to target groupings of users based on their interests.
Invalid clicks:
Also called “Click Fraud,” clicks on ads that are rendered using automatic and sometimes malicious software.
K
Key performance indicator (KPI):
The performance value of your primary metric. It helps you determine if you are reaching your advertising campaign’s goal.
Keywords:
Words, sometimes phrases, that digital marketers such as SEOs and PPC advertisers use to make pages appear higher in search results after users type in a search query that matches keyword exactly or else is related to or relevant to the keyword.
Keyword matching options:
Also called “Match Types.” Keyword level-settings that let you control if your ad triggers for search queries containing your exact keyword phrase, a close keyword phrase, or related keyword phrases. Match types include broad, modified broad, phrase, exact, and negative match types.
Keyword research:
Also called “Keyword Mining.” The process of finding and optimizing for relevant keywords to your target keyword. Identifying a keyword’s user intent is also a part of keyword research.
Keyword planner:
Google’s keyword research tool that helps advertisers to find related keywords and negative keywords, estimates keyword traffic volume, and determines competition pages.
L
Landing page:
The page on your site, marked by your destination URL, where users find themselves after they click on your PPC ad.
Lead:
Potential customers or users who show an interest in your brand, product, or services, but have not yet taken action to convert.
LinkedIn ads:
LinkedIn’s advertising platform where you can advertise on prominent pages on LinkedIn.
Location extensions:
Google Ads feature adds your business address and phone number beneath your PPC ads.
Location targeting:
Google Ads setting that allows you to show your ads to users in specified geographic locations.
Long-tail keywords:
Keyword phrases containing two or more words, like “deep crust pepperoni pizza.” These keywords are more specific than head terms and are often less competitive. Targeting long-tail keywords will help you generate qualified web traffic.
Low search volume:
Keywords with little to no search history on Google Search that will be inactive until searches for them increase.
M
Manual bidding:
Where you set and adjust custom bid amounts without Automatic Bidding activated. Lets you have greater control over maximizing your cost-per-click.
Manual tagging:
Tagging your destination URLs yourself instead of through automated software, which allows for flexibility and customization and can be passed on to third parties.
Marketing metrics:
Measurable values such as conversions, clicks, or leads, that help determine an advertising campaign’s performance.
Message extensions:
Feature on Google Ads adds text messaging capabilities directly to your ad so potential customers can quickly contact you for more information.
Modified broad match:
Also called “Broad Match Modifiers.” Keyword match type that allows you to match keywords more specifically than broad match, but more generally than phrase match or exact match.
My client center (MCC):
Central account for managing multiple Google Ad accounts.
N
Negative keywords:
Also called “Negative Match.” Keywords added to your account indicated that you don’t want your ads to display on the search pages for search queries containing those keywords. Identifying negative keywords will help your ad campaign draw in more qualified clicks.
Negative placement:
Also called “Placement Exclusion.” Similar to how Negative Keywords work, Google Ads lets you determine which ads you want to prevent from appearing on particular sites increase the relevancy of your ads.
New visitor:
An individual who visits your site for the first time.
O
Opportunities tab:
Google Ads tool that suggests options such as budget recommendations and potential keywords to help you develop and maximize your current PPC campaign.
Organic search results:
Search results that appear naturally on search pages in response to users’ search queries. These types of results are not sponsored.
P
Pay-Per-Action (PPA):
Also called “Pay-Per-Acquisition” or “Cost-Per-Action.” The amount of money you pay to a site each time one of your ads hosted on that site leads the user to a purchase.
Pay-Per-Click (PPC):
Pay-per-click (PPC) is an Internet advertising strategy in which advertisers pay their publisher (Google, Bing, etc.) only when their ads are clicked on. This strategy allows advertisers to gain quick visibility with their target users while also maintaining a high return on investment (ROI).
Pay-Per-Click management:
Process of optimizing and tracking PPC campaigns to reach specific goals and minimize expenditures while maximizing returns. Companies often outsource their PPC management to PPC management agencies.
Phrase match:
Lets you display ads only when users’ search queries includes your keyword’s close match.
Pinterest ads:
Pinterest’s advertising platform that lets you target locations, demographics, or devices with promoted pins.
Placement targeting:
Also called “Managed Placement,” lets you target sites in the Partner Network where you want to place ads.
Placement tool:
Google Ad tool that helps you locate targets for ad placement on the Display Network.
Price extensions:
Google Ads feature that showcases a list of products or services and their prices beneath the text of your PPC.
Primary metric:
The measurable value, such as leads, that you determine is most important for your advertising campaign.
Product listing ads (PLA):
Also called “Google Shopping ad,” a type of paid ad that includes more information on products such as images, price, and brand name. Similar to PPC, you only pay when users click on the ad.
Promotion extensions:
Free-to-add Google Ad feature that highlights current sales for your target audience by adding promotional offers beneath text ads.
Prospect:
Lead that qualifies for specific criteria that will move them through the sales funnel. The requirements include that the lead fits your target market and has purchasing means and power.
Q
Qualified web traffic:
Visitors that are genuinely interested in your content, products, or services. They are more likely to convert than more general web traffic.
Quality score:
Ranking system with several disclosed and undisclosed factors that search engine algorithms use to determine the relevancy of keywords compared to their accompanying ads and the landing pages the ads link to. The more relevant the keywords your bid for are to your ad campaign, the higher your ad ranks, and the less the bids cost.
R
Reach:
The total number of users who view an ad.
Remarketing:
Also known as “retargeting,” a marketing campaign that involves showing targeted ads to returning visitors to increase the chances of them converting.
Remarketing lists for search ads (RLSA):
Google Ad feature that enables the targeting of returning visitors with paid search ads explicitly optimized for them.
Returning visitor:
An individual who has visited your site more than once.
Return on ad spend (ROAS):
Ratio determining the amount of money gained (or lost) in comparison to the amount of money invested. Useful when comparing performances of two ad campaigns.
Return on investment (ROI):
Similar to ROAS, a ratio that determines the amount of money gained (or lost), including any expenditures made in the process, in comparison to the amount of money spent. ROI is used to measure how efficient your PPC is performing and to determine whether the investment was worth it.
S
Sales funnel:
Step-by-step process companies guide consumers through where the result is users making a purchase.
Search engine:
Sites like Google or Bing that searchers use to find information. The program uses algorithms and machine learning to create an index of sites that it can pull from to give user’s sites with information relevant to their search queries.
Search engine marketing (SEM):
Online marketing to increase your site’s visibility through paid search advertisements like PPC.
Search engine optimization (SEO):
Set of strategies and tactics such as keyword optimization that improve organic traffic to your site, pushing your site’s rank higher on relevant search pages.
Search engine results page (SERP):
The page that Google returns to users after they enter a search query into the search bar. The page contains a list of links to relevant sites to the user’s query (both organic results and paid ads), as well as any relevant Featured Snippets.
Search network:
A network of sites that partner with Google, as well as Google-owned search sites like Google Maps and Google Images, where you can opt to show your paid ads.
Search marketing:
Umbrella term for online marketing strategies that include search engine optimization, social media marketing, and paid online advertisements meant to increase your site’s visibility in search pages.
Search partners:
Partner sites of Google that agree to show PPC ads for a portion of the profit generated from the ads. When creating a Google Ads campaign, your ads will appear on these sites as well.
Search query:
Also called “search term,” the term or phrase that users enter into a search bar to find information. Your ad will appear on their search page if the query contains the keywords you bid for.
Search query report (SQR):
Also called “search terms report,” reports that are generated by Google Ads that specify how well your targeted keywords are performing against users’ search queries. In other words, the report will identify the search terms users enter before they click on your PPC.
SMB PPC
SMB PPC is a paid ads digital marketing strategy for small to mid-sized businesses (SMBs) in which SMBs pay to have their advertisements shown to users through digital channels.
Search volume:
Estimated number of searches that are expected for a keyword within a specific time frame.
Seller central:
Amazon’s web interface for third-party brands and merchants, allowing them to set product prices and stock items they sell on Amazon. As opposed to Vendor Central, Seller Central enables merchants to sell the products personally on the Amazon site (See Vendor Central).
Seller ratings extension:
Google Ads extension that displays the number of ratings gathered from Google and approved third-party sites on a five-star scale beneath ad text. The extension helps generate quality leads from users making informed decisions and enables you to examine the performance of your ad.
Shared budgets:
Budgeting option for Google Ads to spread your paid ad budget across multiple ad campaigns.
Sitelinks extensions:
Google Ads extension that promotes additional links (with separate URLs from the main one) to your site below the text of the paid ad.
Snapchat ads:
Snapchat’s advertising platform. Ads on Snapchat are self-serviced, 10-second-long, vertical videos that are full-screen and play with sound. Users have the option to swipe to perform an action that will convert them.
Smart bidding:
Subset of automated bidding strategies that enhance conversion and conversion value across your bidding campaign with machine learning. The automatic bids can be tailored to the bidder’s unique context.
Split test:
Also called “A/B testing” or “bucket testing.” Testing two versions of an ad with one slight difference to see which performs more effectively.
Sponsored product ads:
Amazon PPC ads that promote your products in SERPs and product detail pages on Amazon.
Sponsored results:
Also called Sponsored Links and is an alternate term for Google Ads advertisements. Sponsored Results optimized to appear on search pages for targeted search queries.
Structured snippet extensions:
Feature that allows you to show more information on specific products and services beneath your PPC text ad in the form of a header and a list of features.
T
Topic targeting:
Google Ads feature that allows targeting of selected topics instead of keywords or placements and leads to more impressions than conversions.
Tracking code:
Snippet of JavaScript that tracks the activity of a user after they visit a site.
Traffic estimator:
Free Google Ads tool to predict the performance of keywords based on search volume and to research average prices and ad positions.
TrueView video ads:
YouTube video format that gives viewers a choice over which messages they want to see and when and the ability to skip ads, which means you don’t have to pay for unwanted views.
U
Unique visitor:
Individuals who visit a site once within a reporting period.
User:
A person who has the ability to purchase a product or service and to gain information to obtain a benefit or solve a problem.
User ID:
Also called “Username.” A tag that users create to identify themselves on a computer or network.
V
Vendor central:
Amazon’s web interface for manufacturers and distributors to manage and sell their products. The major difference between Vendor Central and Seller Central is that with Vendor Central, Amazon buys and resells the products. A Vendor Central account (by invitation only) is needed to use Amazon Marketing Services (AMS).
View-Through conversion:
Number of online conversions within 30 days. Measures users who see a paid ad but don’t click on the ad but are converted through other means.
View-Through-Rate (VTR):
Ratio for skippable ads measuring the number of completed views against the number of initial impressions.
Visitor:
Any individual that visits a website. Any person that clicks on a PPC ad is considered a visitor. Visitors are split into groups called returning visitors and new visitors.
W
Website optimizer:
Tool to test changes made to the content of your site’s pages. It helps determine what is useful for generating conversions. For example, you use the tool to test different versions of your PPC’s landing page to see which performs better.
Hunting for a top-notch PPC management agency?
Check out what WebFX can do for your PPC advertising campaign!
WebFX is a full-service digital marketing company and search engine marketing agency. We’re a Google Premier Partner, and we’ve generated 24 million qualified leads for our clients in the last five years. With 29 years of experience under our belt, we know how to best drive results for your PPC campaign.
Contact us online or call us 888-601-5359 at for a free quote!
Related Resources
- Google Topics: What is It and How Does It Work?
- How to Prove the Value of Marketing for Your Business
- Marketing Buzzwords: 13 Basic Marketing Terms to Help You Get Started
- Marketing Mix Models: What Are They and How Can You Use Them?
- SEO Glossary
- Social Media Glossary
- Total Addressable Market (TAM): What is It and How Can You Calculate It?
- Web Design Glossary
- Web Development Glossary
- What Are Negative Keywords
Marketing Tips for Niche Industries
- Physician Disability Insurance Marketing
- Plumbing Statistics
- Podiatrist Marketing: How to Stand out and Attract More Patients
- PPC for Labs and Lab Equipment Suppliers
- Private Equity
- Property Management Marketing: 4 Strategies for Growth
- Proven Locksmith Marketing Strategies to Unlock Local Leads & Earn More Jobs
- Reach New Audiences with a Top Medical Device Marketing Agency
- Real Estate Digital Marketing: 6 Tips for Using Online Marketing for Realtors
- Restaurant Marketing Budget
Browse All of Our PPC Resources











